you know how sometimes our homes can have that funky smell from cooking, pets, or even that leftover paint odor? Well, there’s this thing in many air purifiers called an activated carbon filter, and it’s kind of like a superhero for getting rid of those stinky situations. so what is an Activated Carbon Filter ?
Think of activated carbon like a sponge, but a really, really fine one. When air passes through it, all the nasty particles and smells get “stuck” inside it. This isn’t like a sponge soaking up water though – it’s more like how a magnet attracts metal. They call this process “adsorption” – yeah, with a ‘d’, not a typo!
The cool thing is, it’s not just for air. This activated carbon magic is used in water filters too, like in our water pitchers or even in bigger industries.
So, if you’re ever tired of those stubborn smells in your place, maybe from last night’s fish fry or your cute pet’s not-so-cute odors, think about getting an air purifier with this activated carbon filter. It doesn’t just make your home smell better, but it also pulls out harmful stuff from the air, making it healthier for us. Before buying one, we can chat more about the different types and what to look out for. Sound good?
What is Activated Carbon?
Activated carbon, sometimes referred to as activated charcoal or active carbon, is a form of carbon processed to have small, low-volume pores. These pores increase the surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions. Due to its high degree of microporosity, one gram of activated carbon has a surface area in excess of 3,000 m^2 (32,000 sq ft), as determined by gas adsorption.
How is Activated Carbon Produced?
The production of activated carbon involves two main stages:
- Carbonization: Raw materials, such as coconut shells, wood, peat, sawdust, or other carbon-rich materials, are subjected to high temperatures in an inert atmosphere to produce a char. This char contains a mix of fused and un-fused carbon particles.
- Activation: The char undergoes an “activation” process. This involves treating it with an activating agent, often phosphoric acid, at high temperatures. This process removes any remaining non-carbon elements and further develops the internal pore structure, increasing its surface area.
How Does an Activated Carbon Filter Work?
The primary mechanism by which activated carbon filters work is through adsorption. Here’s a step-by-step explanation:
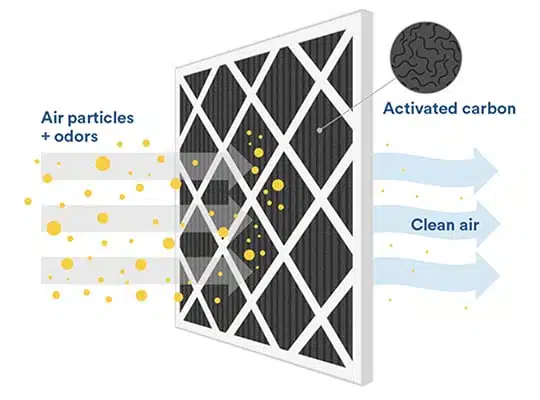
- Contact: As water or air passes over the activated carbon, contaminants are drawn and held by the carbon surface. This is due to the carbon’s vast surface area being electrically charged, which attracts and captures these contaminants.
- Adsorption: Unlike absorption, where a fluid is dissolved by a liquid or solid, adsorption is the process by which atoms, ions, or molecules adhere to a surface. The contaminants become attached to the carbon particles.
- Pore Size Distribution: The effectiveness of activated carbon is also attributed to its pore size distribution. The carbon particles contain various pore sizes, with larger pores trapping larger contaminants and smaller pores trapping smaller contaminants.
- Regeneration and Lifespan: Over time, the pores of the activated carbon can become filled with adsorbed contaminants, reducing its effectiveness. Depending on the application, the filter may need to be replaced or regenerated by cleaning.
Adsorption vs. Absorption: Breaking it Down
Adsorption: Imagine you have a magnet and you hover it over some metal paperclips. Those paperclips will stick to the magnet’s surface. This is similar to adsorption – where contaminants stick to the outer surface of something (like carbon in our example).
Absorption: Think of a sponge soaking up spilled water. The water goes inside the sponge and becomes part of it. That’s like absorption – where something is taken in and becomes part of the structure.
In the context of the activated carbon filter:
- Adsorption lets the filter capture and hold onto harmful gases from the air because they stick to the carbon’s outer surface.
- However, over time, just like a magnet can only pick up a limited number of paperclips, the carbon filter can get “full” and won’t be able to capture any more contaminants. So, a filter with more carbon can catch more contaminants and lasts longer.
I hope that makes things clearer!
Applications of Activated Carbon Filters:
- Water Purification: Activated carbon filters can remove chlorine, sediment, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), taste, and odor from water. They are commonly found in household water filtration systems and aquariums.
- Air Purification: Activated carbon is effective at adsorbing gaseous pollutants and odors, making it a staple in air purifiers and HVAC systems.
- Medical Uses: Activated carbon is used in gas masks and respirators to protect against toxic gases. It’s also used in certain medical treatments, like treating poisonings and overdoses.
- Industrial Applications: Industries utilize activated carbon filters to capture waste gases and effluents, ensuring that harmful emissions don’t reach the environment.
What is activated charcoal
Activated charcoal is essentially super-charged charcoal. By treating it with oxygen, tons of tiny pores pop up between its carbon atoms. This process boosts its surface area enormously, allowing it to have up to 2,000 square meters of surface per gram. Because of this, activated charcoal is like a magnet for certain impurities.
The key term is “adsorb” – when substances come close to this charcoal, they get attracted and stick to it. It’s great for catching carbon-based contaminants and even chlorine. But remember, it’s selective. Some chemicals, like sodium or nitrates, won’t be captured. And once all its “sticky spots” are filled, the filter needs replacing. So, in short, it’s a selective, super-effective filter until it’s full!
Choosing the Right Activated Carbon Filter: A Simple Guide
Looking for an air purifier? The kind of carbon filter it uses can make a big difference, especially when it comes to getting rid of bad smells.
There are mainly two types of carbon filters:
- Pellet-based Carbon Filter: Think of this as a powerhouse for tackling bad odors. It’s filled with tiny carbon pellets that are really good at trapping and neutralizing smells.
- Fibrous Filter Coated with Carbon: This one’s more like a light sweater with a sprinkle of carbon on it. It does help with odors but not as much as the pellet-based one.
From my own tests with a bunch of air purifiers, the pellet-based filters are usually the winners in the odor-fighting game.
Beyond just odor removal, carbon filters, especially the pellet-based ones, have shown efficiency in capturing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) – these are the sneaky chemicals that can come from things like paint or cleaning supplies. Plus, many experts recommend pellet-based filters for spaces where strong odors are common, like kitchens or rooms where you might keep litter boxes.
In short, if getting rid of strong odors is your top priority, go for the pellet-based carbon filter. If you just need a general clean-up, a fibrous filter with carbon might do the trick!
FAQ
1. What exactly is an activated carbon filter?
Activated carbon filters, made from carbon that’s undergone a special process to open up its pores, effectively neutralize bad odors and trap harmful gases like VOCs and formaldehyde.
2. I’ve heard “activated charcoal” and “activated carbon.” Are they the same?
Yes! Whether it’s called activated charcoal or activated carbon, it’s essentially the same filter. Brands might use different terms, but the function remains consistent.
3. Can I wash my activated carbon filter to make it last longer?
Typically, it’s not advised. While some manufacturers might suggest giving their filters a refresh, washing can affect their efficiency. Always check the manufacturer’s recommendations.
4. How frequently should I replace the activated carbon filter in my purifier?
The lifespan of these filters can vary, but generally, they should be replaced every 6 months to maintain optimum performance. However, in some cases, with less polluted environments, they might stretch up to a year.
5. How do these filters manage to capture bad odors and gases?
The secret is “adsorption.” Activated carbon filters have a vast porous surface that chemically attracts and traps pollutants, effectively cleaning the air.
6. Are there any safety concerns with using activated carbon filters?
No worries there! Activated carbon filters are widely recognized as safe, with applications spanning from medical treatments to cosmetics and home air purification.
7. What’s the difference between adsorption and absorption?
Great question! While they sound similar, adsorption is about pollutants sticking to the surface of the carbon. In contrast, absorption is when something is soaked up entirely into another substance.
8. Can activated carbon filters remove allergens like pollen or pet dander?
Activated carbon filters are excellent for gases and odors. For particles like pollen or pet dander, you’d typically need a HEPA filter, often paired with carbon filters in many air purifiers.
9. Do activated carbon filters produce ozone?
No, activated carbon filters do not produce ozone. They simply trap and neutralize pollutants.
10. Are there any downsides to using activated carbon filters?
The primary thing to remember is that once their “adsorption” capacity is maxed out, they need to be replaced to remain effective. Over time, if overloaded with pollutants, their performance can decrease.
Remember, when choosing an air purifier or any filter system, it’s always good to consider your specific needs and consult manufacturer guidelines.