one term you may have come across is the ‘HEPA filter’. Standing as a beacon of high-efficiency particulate air filtering, the HEPA filter is often hailed as the gold standard in air purification. But what is a HEPA filter, and why is it so revered in various industries, from homes and hospitals to nuclear facilities and the food industry?
This blog aims to define the concept of the HEPA filter, exploring its origins, how it works, and its various applications. We’ll delve into the science behind its ability to trap airborne particles down to minuscule sizes measured in microns. We’ll also discuss the importance of regular filter replacement to maintain its high efficiency and the difference between a True HEPA filter and other filters that may claim the HEPA label.
Whether you’re considering investing in an air purifier, a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter, or just curious about this air-filtering technology, this blog will provide you with the insights you need. So, let’s embark on this journey to understand the HEPA filter – the cornerstone of clean air.
What Does HEPA Mean?
HEPA, an acronym for High-Efficiency Particulate Air, represents a standard for air filter efficiency. However, it’s crucial to differentiate between true HEPA filters and other variants such as HEPA-like, HEPA style, or HEPA type filters. Some manufacturers may label their filters as 99% HEPA or simply HEPA, even if they don’t pass the stringent tests to qualify as such. To counteract these false claims, many brands that successfully pass the HEPA test now label their filters as True HEPA.
What is a HEPA filter?

A HEPA filter is a specially designed pleated mechanical air filter that excels in trapping airborne particles. According to the official definition by the U.S. Department of Energy, a true HEPA filter can theoretically eliminate at least 99.97% of dust, pollen, mold, bacteria, and any airborne particles as small as 0.3 microns (µm). This specific diameter of 0.3 microns is not chosen at random; it represents the Most Penetrating Particle Size (MPPS), which is the most challenging size of particle for a filter to capture. Interestingly, particles that are either larger or smaller than 0.3 microns are trapped with even higher efficiency.
It’s important to note that all air cleaners, including those with HEPA filters, require regular cleaning and filter replacement to maintain their effectiveness. Always adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding maintenance and filter replacement.
Lastly, the term MERV, standing for Minimum Efficiency Reporting Values, is used to indicate a filter’s capability to capture larger particles between 0.3 and 10 microns (µm). This rating is another important factor to consider when evaluating the efficiency of air filters.
| MERV Rating | Average Particle Size Efficiency in Microns |
|---|---|
| 1-4 | 3.0 – 10.0 less then 20% |
| 6 | 3.0 – 10.0 49.9% |
| 8 | 3.0 – 10.0 84.9% |
| 10 | 1.0 – 3.0 50% – 64.9%, 3.0 – 10.0 85% or greater |
| 12 | 1.0 – 3.0 80% – 89.9%, 3.0 – 10.0 90% or greater |
| 14 | 0.3 – 1.0 75% – 84%, 1.0 – 3.0 90% or greater |
| 16 | 0.3 – 1.0 75% or greater |
HEPA Filter Working
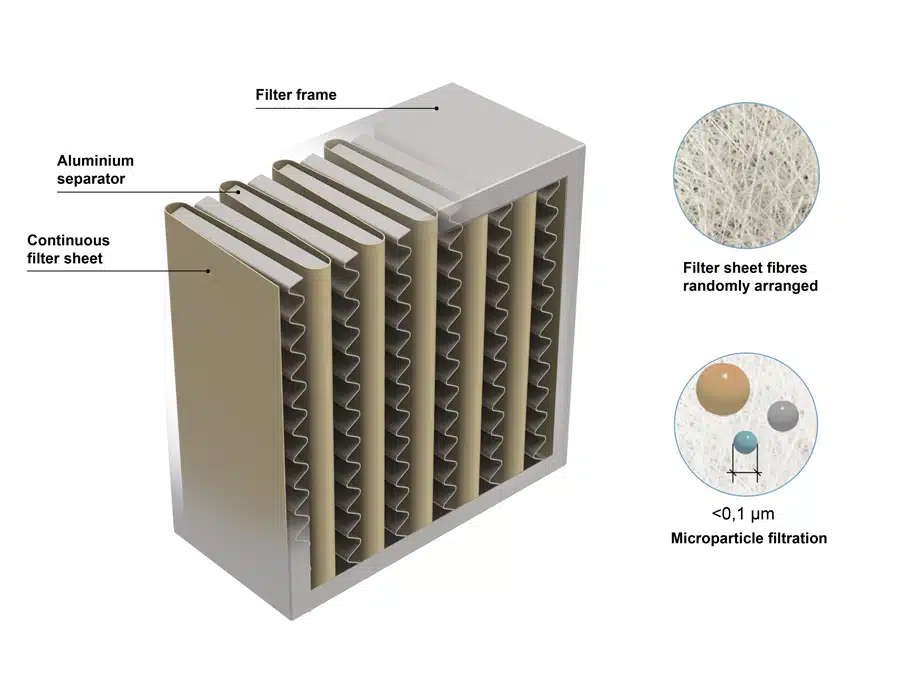
A HEPA filter, unlike a standard air filter, is a thick, pleated mechanical filter designed to trap a wide range of particle sizes. The pleats form a dense, randomly arranged mat of fibers that effectively capture particles as air passes through the filter. This capture process involves three mechanisms: diffusion, interception, and impaction.
Diffusion is a process where smaller gas molecules, less than 0.1 microns in size, collide with each other, causing a delay in their passage through the filter. This delay increases the chances of the particles being trapped by the next two mechanisms. Interception happens when particles flowing with the air stream adhere to a fiber. Impaction, on the other hand, occurs when larger particles directly embed themselves into the fibers.
To prolong the life of a HEPA filter, a pre-filter can be used to remove larger particles, leaving the finer particles to be trapped by the HEPA filter. For instance, commercial air purifier units from ISO-Aire come with MERV-8 pre-filters to extend the lifespan of the HEPA filter.
HEPA filters work by capturing particles entering the filtration device, often using fans to draw air into the system. A True HEPA filter can capture 99.97% of airborne particles down to 0.3 microns, while the standard in the European Union is slightly lower at 99.95%.
The process of particle capture in a HEPA filter can be further broken down into four methods:
- Direct Impact: Larger particles are trapped when they directly hit and stick to the filter.
- Sieving: Particles larger than the gaps in the filter get stuck in these holes.
- Interception: Smaller particles that could pass through the gaps are instead adhered to the side of a fiber due to the inertia of the air pulling them.
- Diffusion: Ultrafine particles, which are light and move quickly, are likely to hit a fiber and stick to it due to their erratic movement.
How does HEPA filters are different
Not all HEPA filters are the same. They can differ in several ways, including their efficiency standards and the specific particles they can trap.
In the United States, a HEPA filter is required to capture 99.97% of airborne particles larger than 0.3 microns to meet the standard. In contrast, the standard in Europe is slightly lower, requiring a HEPA filter to capture 99.95% of such particles.
However, it’s important to note that not all filters labeled as “HEPA” meet these standards. Some filters may be marketed as HEPA, but they have not undergone the necessary testing or do not meet the required efficiency standards. Therefore, it’s crucial to read the specific ratings of a filter to ensure it is a true HEPA standard filter.
Another term you might come across is “True HEPA.” This term is used by marketers to indicate that a filter meets the actual HEPA standard. On the other hand, filters labeled as “HEPA-like” or “HEPA-type” may not meet the HEPA standard requirements. These filters can remove between 85% to 99% of airborne particles down to 0.3 microns. While they are not as effective as true HEPA filters, they are typically more affordable and can still serve a purpose in certain situations.
Additionally, HEPA filters can also be rated using the MERV (Minimum Efficiency Reporting Values) system. This rating measures a filter’s efficiency in capturing particles between 0.3 and 10 microns. In the United States, a HEPA filter needs to meet at least a MERV rating of 17 to be considered a HEPA filter, while in the European Union, a MERV 16 rating is considered a HEPA filter.
Lastly, it’s worth noting that HEPA filters require regular replacement to maintain their efficiency. The replacement frequency can vary depending on the filter model and the level of pollution in the operating environment, but it typically ranges from every 6 to 18 months.
What Is a MERV Rating?
MERV, an acronym for Minimum Efficiency Reporting Values, is a rating system used to evaluate the efficiency of air filters in trapping particles ranging from 0.3 to 10 microns in size. The higher the MERV rating, the more efficient the filter is at capturing these particles. In the context of HEPA filters, a minimum MERV rating of 17 is required for a filter to qualify as a HEPA filter in the United States. However, in the European Union, a filter can be considered a HEPA filter with a slightly lower MERV rating of 16.
HEPA Filter Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Effectiveness: HEPA filters are known to be highly effective in filtering air. They can capture at least 99.97% of particles that are 0.3 microns in diameter.
- Versatility: They are used in a variety of settings, including homes, hospitals, industries, and vehicles. They are also found in many consumer products like air purifiers and vacuum cleaners.
Cons:
- Cost: HEPA filters can be more expensive than other types of filters, both in terms of initial cost and the need for regular replacement.
- Limited Scope: While HEPA filters are excellent at removing particulates like dust, pollen, and mold spores, they are not designed to remove odors or chemical pollutants. For these, additional types of filters or air purifiers may be needed.
- Maintenance: HEPA filters cannot be washed or vacuumed, as this can damage the filter structure and reduce its efficiency. They need to be replaced regularly to maintain their effectiveness.
Can You Wash HEPA Filter?
By no means you can not wash the HEPA filter. HEPA filters are designed in a particular way, and every interference with the filter may damage the filter structure, and your HEPA filter may act as a regular filter. In other words, if you damage the filter in any way, it won’t have HEPA standard efficiency. Because of that, we are not washing HEPA filters. If for some reason, your manufacturer labeled HEPA filter as washable, I would double-check if I really own a True HEPA filter. And if I really do have HEPA standard filter, I would still not wash it.
FAQ
What does HEPA stand for?
High-Efficiency Particulate Air.
What is a HEPA filter?
A HEPA filter is a type of mechanical air filter that can trap at least 99.97% of dust, pollen, mold, bacteria, and any airborne particles with a size of 0.3 microns.
What is the difference between a HEPA filter and a regular filter?
A HEPA filter can trap a significantly higher percentage of small particles compared to regular filters, making it more effective for improving air quality.
Can a HEPA filter remove odors?
No, HEPA filters are designed to remove particles from the air, not odors. For odor removal, other types of filters or air purifiers may be needed.
Can I wash or vacuum my HEPA filter?
No, washing or vacuuming a HEPA filter can damage its structure and reduce its efficiency. HEPA filters should be replaced when they become dirty.
How often should I replace my HEPA filter?
The frequency of replacement depends on the specific model and the level of pollution in the operating environment, but typically ranges from every 6 to 18 months.
What is a True HEPA filter?
A True HEPA filter meets the official HEPA standard of capturing at least 99.97% of particles that are 0.3 microns in diameter.
What is a MERV rating?
MERV, or Minimum Efficiency Reporting Values, is a rating system that measures a filter’s efficiency in capturing particles between 0.3 and 10 microns.
Can a HEPA filter capture viruses?
Yes, many viruses are small enough to be captured by a HEPA filter. However, it’s important to note that air filtration is just one part of preventing viral transmission.
Are all HEPA filters the same?
No, not all filters labeled as “HEPA” meet the official standards. Some filters may be marketed as HEPA, but they have not undergone the necessary testing or do not meet the required efficiency standards. Always read the specific ratings of a filter to ensure it is a true HEPA standard filter.