In this post I am going to be answering one of the most common questions regarding air ionizers – do air ionizers REALLY work?
Here is the short version of the answer: yes, air ionizers work (and they work GREAT), but only if they have a high enough negative ion emission. The higher the negative ion emission (measured in cm3/second), the better an air ionizer will work.
If you jump into the air purifying world you will sooner or later come across devices called “negative ion generators” – or air ionizers for short. With so many different types of air purifiers out there, it is hard to differentiate what is effective and what is not. There are many devices that people label as air ionizers, which is only half-true. Some of these devices perform very poorly, so you can find a lot of conflicting opinions regarding their effectiveness. All air ionizers are air purifiers, but not all air purifiers are ionizers.
In order for me to fully explain and answer the main “do air ionizers really work” question, I need to explain a couple of things first. You need to understand how air ionizers work, different types of air ionizers, and the most important factors regarding their effectiveness.
I did not include any other aspects of air ionizers in this thread, such as negatives and positives, difference between air ionizers and purifiers, and so on. I focused purely on answering this specific question.
Let’s begin.
How do air ionizers work?
While I am not going to be spending too much time on this part, it is necessary to understand. You first need to understand the basic principle behind how air ionizers work, if you want to be able to answer if they really do work. The picture below illustrates the “how” part in 4 simple steps:
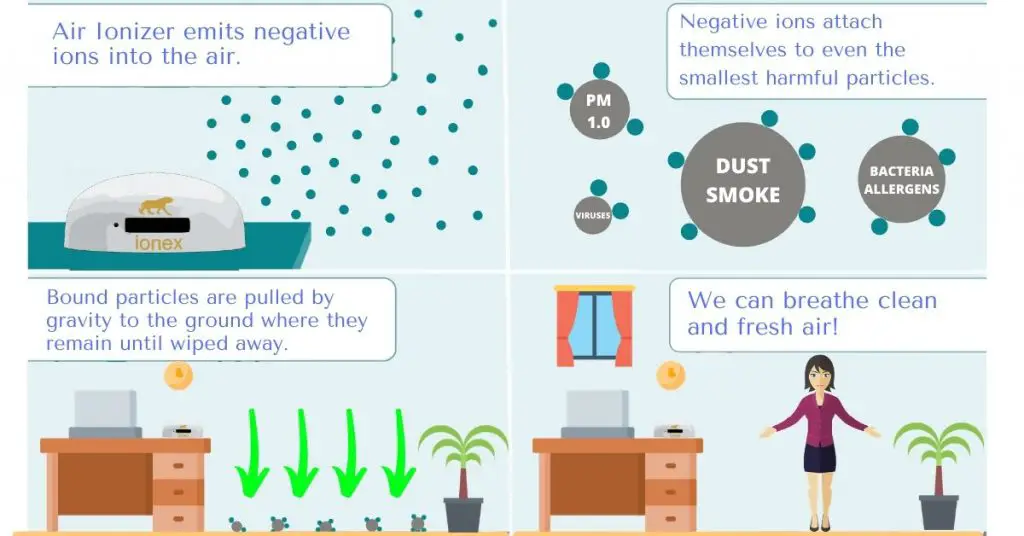
Source: ionex-ionizers.com
As you can see from the picture, the process is pretty straightforward. A negative ion generator (air ionizer) releases a large number of negative ions in the air. These negative ions are not “stable” by themselves and need to attach themselves to natural/positive particles. Luckily for us, harmful particles/pollutants in the air are positively charged! So once negative ions attach themselves to these pollutants, the combined mass becomes big enough for gravity to pull down. Once this mass is on the ground, it can not rise back up in the air. Consequently, we can not inhale these particles into our lungs, which is a great thing for our overall health.
Negative ions and air pollutants
As you know, there are many different sizes of pollutants in the air. In the table below, I have included the most common ones and their sizes. We measure these pollutants in microns. To give a point of reference – human hair has a diameter of around 75 microns.
Common Indoor Pollutant | Particles Size in Microns |
Pollen, mold and plant spores | 7-70 |
Dust mites | 3-10 |
Hairspray | 3-10 |
Large bacteria | 1-20 |
Lead dust | 1-3 |
Auto emissions | 1-3 |
Fungal spores | 0.5-7 |
Cooking odors | 0.3-1 |
Dust | 0.2-8 |
Pet dander | 0.15-8 |
Small bacteria | 0.08-1 |
Tobacco smoke | 0.008-0.6 |
Viruses | 0.005-0.001 |
VOC (volatile organic compounds) | Less than 0.001 |
As you can see from the graph, these particles can get quite small! Now the beautiful thing about negative ions is that they do not care about particle size. This means that they attach themselves to even the smallest particles that are 0.001 microns in size. In comparison, the vast majority of HEPA filters can only deal with particles that are 0.3 microns or bigger. This means that the smallest particles (such as bacteria an virsues) do not get captured effectively by these filters. I chose HEPA filters as a comparison here because they are the industry standard, and the most popular type of air purifiers that people buy – by far.
So in theory, air ionizers have better cleaning capabilities than any HEPA filter, as they remove even smaller pollutants. But if air ionizers really do work, then why are there so many negative opinions about them? Why do many negative ion generators have bad reviews? Great question. Let us look at the next missing piece of the puzzle.
Different types of air ionizers
This is a key part in answering the main question of “do air ionizers really work?”. There are 2 main categories of air ionizer: regular, standalone air ionizers and air purifiers with an added negative ion generator.
Both of these are negative ion generators, but with one big difference. Regular air ionizers are devices that clean the air solely with negative ions. And on the other hand we have air purifiers with an added negative generator, which use negative ions only as a secondary cleaning option. The latter are usually devices that use HEPA filters as their main method of cleaning, and a negative ion generator as a bonus filtering system. While both of these are technically air ionizers, one is an actual stadalon unit, while the other one is an addon.
Air ionizer type and effectiveness
On paper, there should be no major difference however, this is not correct. By far, the biggest factor in air ionizer effectiveness is the emission of negative ions. This is just a fancy way of saying how many negative ions can the air ionizer produce. We measure this in seconds, per cm3. Why is this such a huge deal? Well, there is an enormous amount of harmful particles in the air. And every such harmful particle/pollutant needs at least one negative ion to attach to. If the negative ion generator produces a small number of negative ions, then you will only purify a small amount of air. Consequently, you will not notice any great results.
This brings us back to the previous paragraph. Only a regular, standalone ionizer has the capability of producing enough negative ions to be effective. On the other hand, the vast majority of air purifiers with an ionic feature do not have a high enough negative ion emission for efficient results. In my experience, the bare minimum emission of negative ions should be at least 7-8 million negative ions per second, per cm3.
Do air ionizers really work? – putting it all together
We are finally ready to consolidate all of the information that we wrote above. To recap: you learned that negative ion generators release a huge amount of negative ions into the air. These negative ions then remove even the smallest air pollutants from the air, by attaching themselves to them. Despite their ability to remove even the smallest air pollutants, air ionizers need to produce a high enough amount of negative ions, in order to be effective. Therefore, the bigger the room, the more negative ions an air ionizer needs to emot. For a smaller room, I recommend at least 6-8 million negative ions per second/cm3.
There also an increasing amount of published scientific studies that support the superior cleaning capabilities of air ionizers. Many such popular older articles had the opposite claim, that air ionizers do not do very much in terms of air cleaning. However, as technology progressed so did negative ion generator capabilities. These days, negative ions have a much higher negative ion emission than their predecessors had 10 or even 5 years ago.
Since there are many “bad” air ionizers on the market these days, I have prepared a list of my top 5 best air ionizers to get in 2020. Feel free to check it out if you are in the market for a new air ionizer.
We hope you enjoyed our post and learned something new today!
